Introduction to CaesarCipher.org
Overview
CaesarCipher.org is a practical hub for learning and experimenting with classical cryptography—starting from the Caesar cipher and extending across other historical techniques. It pairs intuitive, browser-based tools with clear explanations, giving students, educators, puzzle makers, and hobbyists an accessible way to encode, decode, and analyze messages while understanding the underlying math and limitations.
Key Features
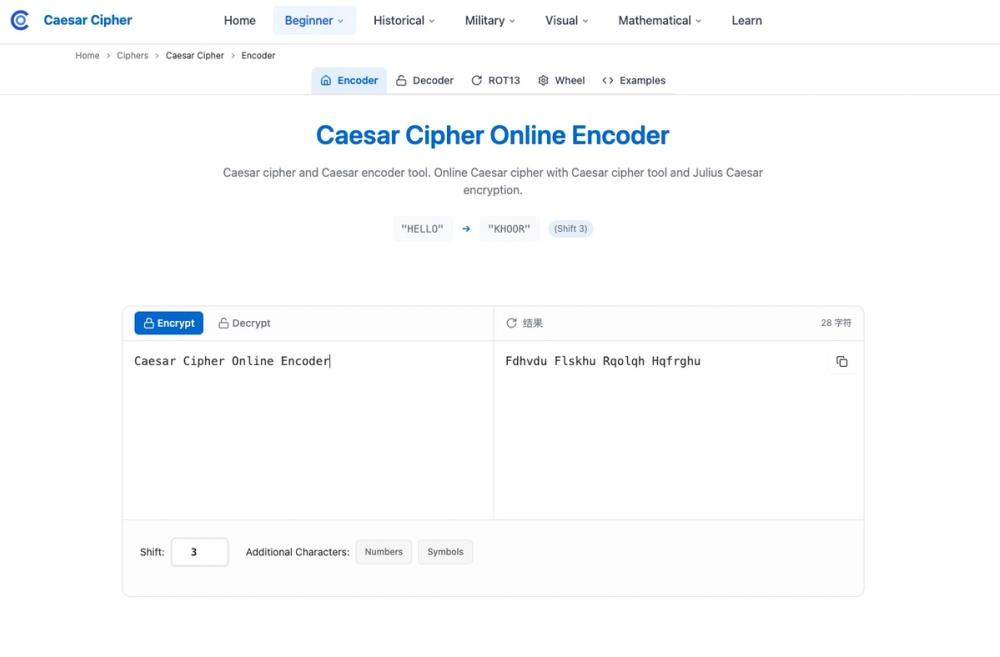
- Caesar Encoder/Decoder
Encrypt and decrypt instantly with custom shift values (including ROT presets like ROT13). Options typically include handling spaces, punctuation, and numbers. - Auto-Cracker / Frequency Analysis
Try all shifts automatically, score likely plaintexts, and visualize why simple substitution is insecure. - ROT Tools (ROT13/47/5)
One-click, self-inverse transforms for quick tests and demonstrations. - Interactive Cipher Wheel
A visual alphabet ring to show wrap-around and letter mapping, perfect for classroom demos. - Examples & Snippets
Copy-ready code and walkthroughs for implementing Caesar and related ciphers. - Learn Library (Growing)
Articles, history notes, practice problems, and references spanning monoalphabetic and polyalphabetic families.
Use Cases
- Classroom & Workshops
Live-demo encoding, decoding, and cracking; connect modular arithmetic (mod 26) to real outputs. - Self-Study & Exam Prep
Start with Caesar, then deepen via tutorials, exercises, and comparisons to other classical ciphers. - Puzzles & Games
Design challenges with Caesar/ROT variants and verify solvability using the auto-cracker. - Programming Exercises
Implement encoders/decoders, compare brute-force approaches, and benchmark key-space searches. - Historical Context
Contrast classical substitutions with modern cryptography to understand why the former is educational, not secure.
Getting Started
- Open the Caesar tool.
Enter sample text likeHELLOand set a shift of3to seeKHOOR. - Toggle options.
Decide whether to include numbers, punctuation, or preserve casing to match your use case. - Explore presets.
Try ROT13 or ROT47 to see self-inverse behavior (applying twice returns the original). - Use the auto-cracker.
Paste a ciphertext and run automatic analysis to reveal the most likely plaintexts, along with scores. - Spin the cipher wheel.
Map letters visually to reinforce modular arithmetic and wrap-around logic. - Read and practice.
Browse the Learn library for deeper explanations, printable references, and exercises.
Tips for Effective Learning
- Iterate quickly: Short inputs reveal how shifts affect patterns.
- Check letter frequencies: Spot common letters (E, T, A, O) to guide manual cracking.
- Vary datasets: Try natural text, code snippets, and puzzle phrases to see different distributions.
- Compare ciphers: After Caesar, test Vigenère, Affine, or Atbash to feel the leap in complexity.
Who It’s For
- Educators needing visual, hands-on demos and ready-to-assign exercises.
- Students & Hobbyists seeking a gentle, tool-first path into cryptography.
- Puzzle Creators & Game Designers prototyping classical cipher challenges.
- Developers integrating simple cipher logic or teaching fundamentals.
Scope and Limitations
Caesar and similar classical ciphers are not secure for modern communications. Their value here is pedagogical: they teach substitution, frequency, and modular arithmetic, serving as stepping stones toward contemporary cryptography (e.g., authenticated encryption, key exchange, and public-key systems). Use the cracking tools as a lesson in why fixed-shift methods fail.